How Are Rates Ratios And Proportions Used In Healthcare
Rates and ratios used to measure health status including geographical occupational socio-economic position and other socio-demographic variations Routine notification and registration systems for births deaths and specific diseases including cancer and other morbidity registers. If the patient weighs 52kg then the patient receives 0025 52 13mg per minute.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Tier_1_Leverage_Ratio_Definition_Nov_2020-01-4741405e9a8f49b79939f1a51fc3de54.jpg)
Tier 1 Leverage Ratio Definition
Health care plays a vital role in protecting and promoting the publics health along with public health organizations.
How are rates ratios and proportions used in healthcare. Plain numbers of events such as deaths or births or hospital admissions have very little meaning in themselves lacking a context in which they can be interpreted. For example 70 influenza case-patients in March 2005 reported in County A. 16 Ratio rate and proportion EMGT What is a ratio.
EMGV A ratio is a comparison of two or more numbers that are usually of the same type or measurement. This is the goal. Sures used with dichotomous variablesare ratios proportions and rates.
Proportion is a ratio in which the numerator is a subset or part of the denominator and can be written as aab A relative frequency A rate is a ratio of the form a ab a the frequency of events during a certain time period ab the number at risk of the event during that time period A rate may or may not be a proportion. It does so by dividing the risk incidence proportion attack rate in group 1 by. Now - how much of the drug do you give each person.
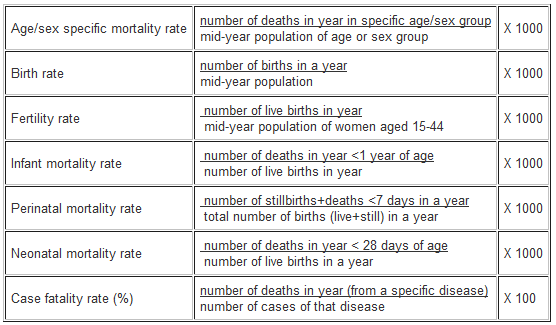
A case-fatality rate is the proportion of persons with the disease who die from it. You give a drug to a patient to achieve a certain level of the drug in for example the blood stream. This is expressed parts per eg.
Numerator is always included in denominator. Relation of size between two random quantities. We write the numbers in a ratio with a colon between them.
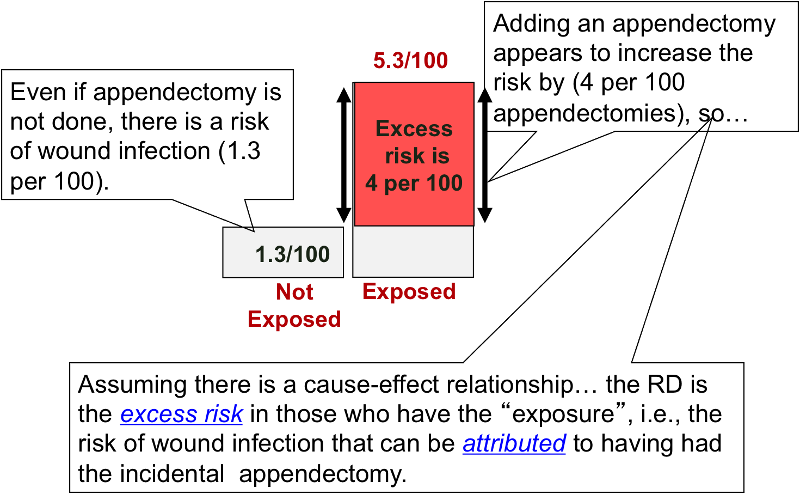
Rates and ratios are cornerstones in understanding the health morbidity and mortality of populations. A risk ratio RR also called relative risk compares the risk of a health event disease injury risk factor or death among one group with the risk among another group. Ratios Proportions Rates Last modified by.
An alternative and more accurate phrase for attack rate is incidence proportion A prevalence rate is the proportion of the population that has a health condition at a point in time. Once a ratio has been identified it is easy to write a proportion to find a solution or the answer to a question. Nurses use ratios and proportions daily as well as converting important units.
The ratios show where operating costs are moving. This is where you really need to use ratios. The numerator is not a component of denominator.
In passive surveillance the physician laboratory or other health care provider ie the reporter takes the initiative in submitting the report by following the list of reportable diseases in that state. 10n is read as 10 to the nth power The size of 10 n may equal for example 1 10 100 or 1000. For example one death due to meningitis.
PROPORTION Is a ratio which indicates the relation in magnitude of a part of the whole. If the numbers have different units it is important to convert the units to be the same before doing any calculations. Tracking and analyzing financial ratios is a critical practice for health care organizations.
Ratios Proportions Rates Last modified by. Ratio proportion rate nxy 10 In this formula x and y are the two quantities being compared and x is divided by y. Public health focuses on populations while clinical care focuses on the individual patient.
Sex ratio doctor-population ratio child- women ratio. The health department or health agency waits for reports to be submitted by others. Doreys Algebra Handbook - A comprehensive guide.
Health care uses ratios in determining medication dosages and additives to IV solutions and in reporting laboratory values and disease statistics. Million - really a proportion of the blood which is the drug. All three mea-sures are based on the same formula.
There are 60 minutes in an hour so in one hour the patient should receive 13 60 78mg. Learn about ratios percents and proportions and see how they can be used in solving problems. The two have differences that are worth highlighting here.
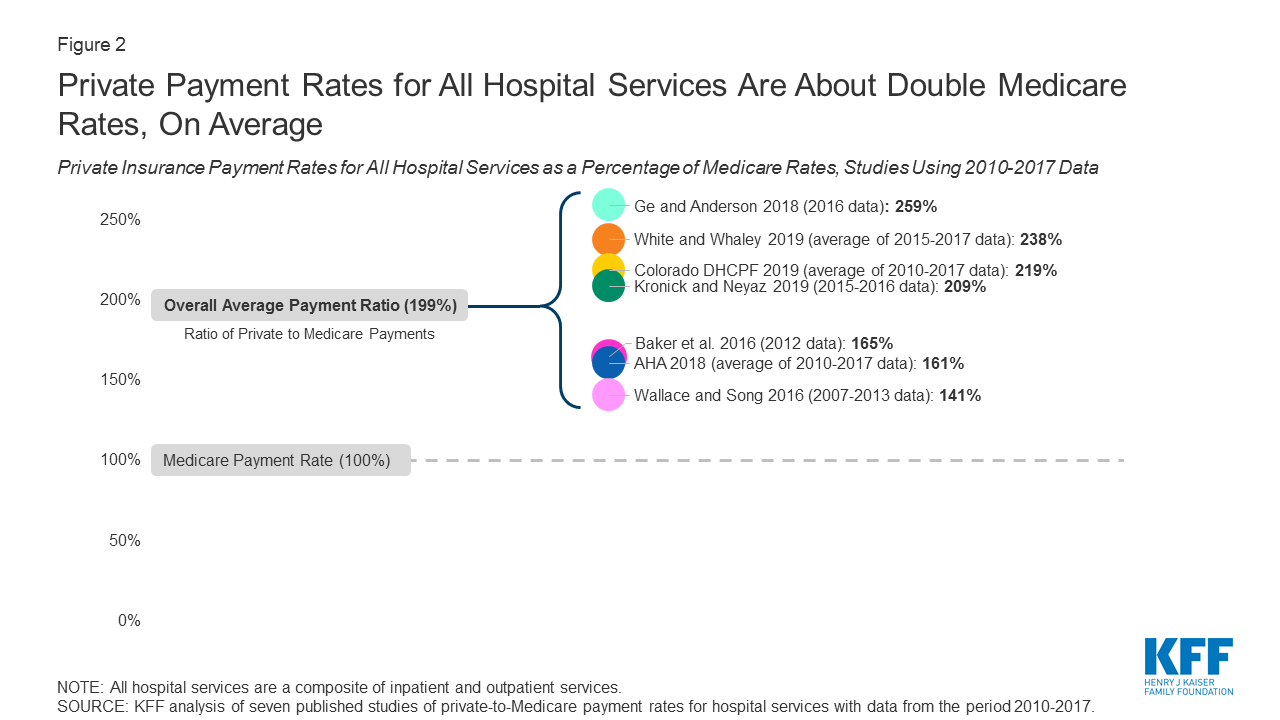
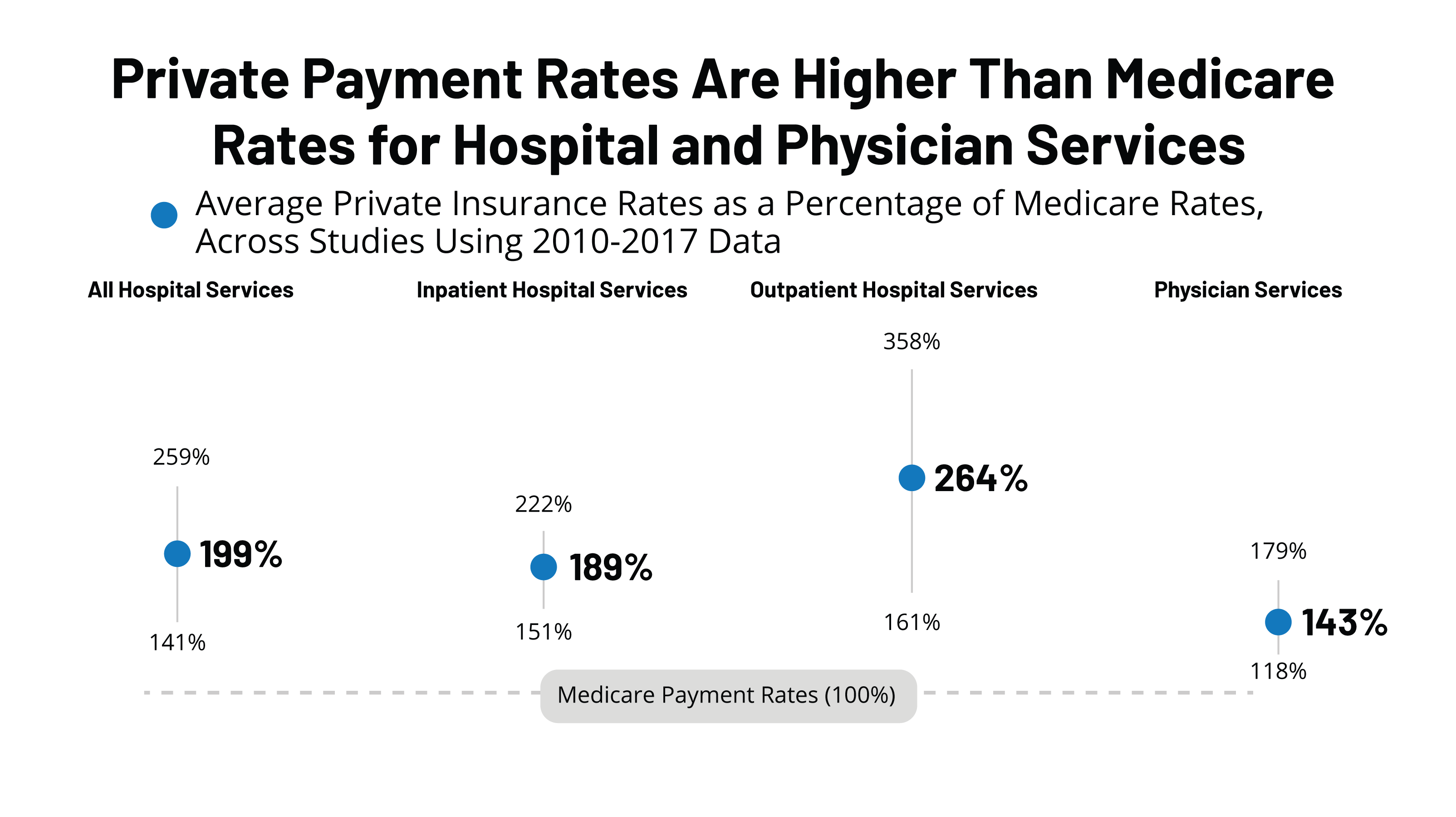
How Much More Than Medicare Do Private Insurers Pay A Review Of The Literature Kff

Unit Rate What Is A Unit Rate Math Tutorvista Com Unit Rate Ratio And Proportion Math Curriculum

How Much More Than Medicare Do Private Insurers Pay A Review Of The Literature Kff
/dotdash_INV_final_Capitalization_Ratios_Jan_2021-01-39b098a2a4f645ddb752bbd1887a488c.jpg)
Capitalization Ratios Definition
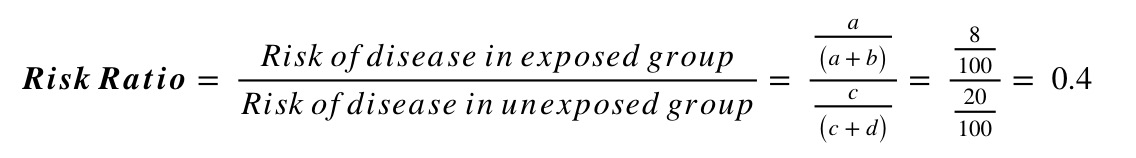
Numerators Denominators And Populations At Risk Health Knowledge
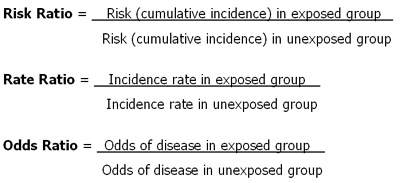
Measures Of Disease Frequency And Disease Burden Health Knowledge

Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio Defined Formula Examples Netsuite

Medical Error Statistics When Healthcare Can Kill You Etactics

Calculation Of Dosages Calculation Of Dosage One Method Nursecepts Med Math Nursing Math Paramedic School

Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training
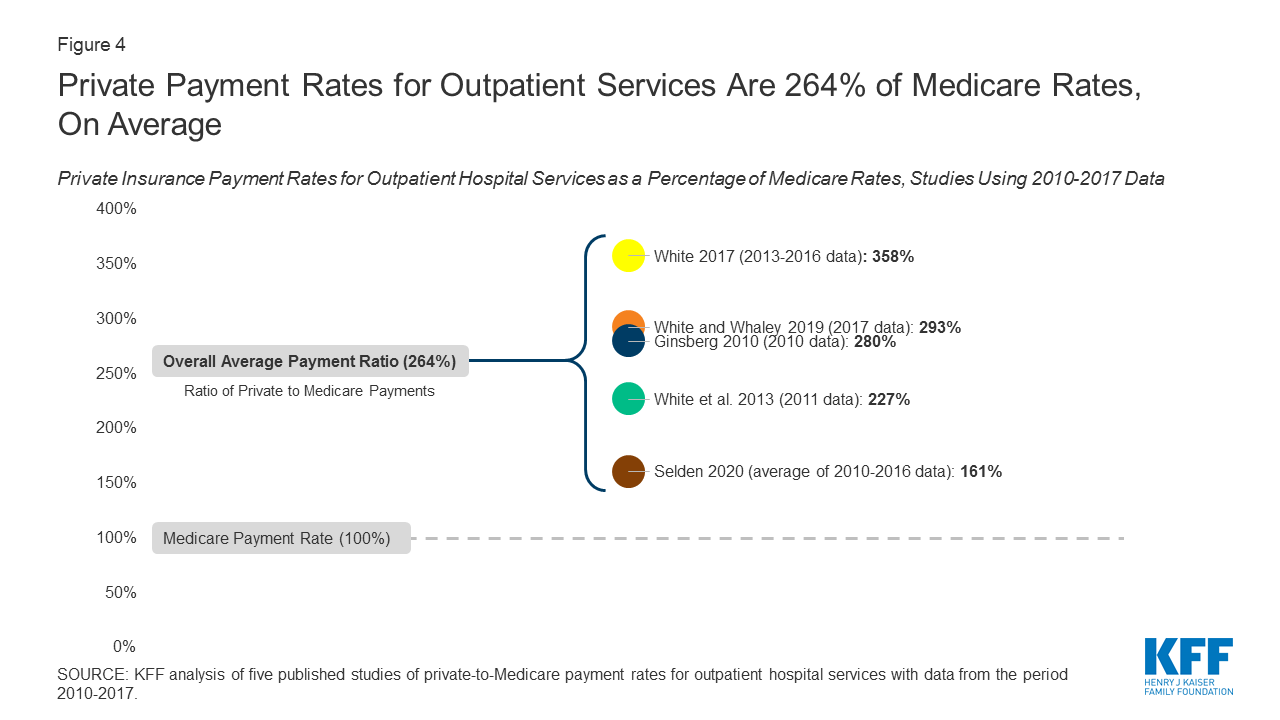
How Much More Than Medicare Do Private Insurers Pay A Review Of The Literature Kff
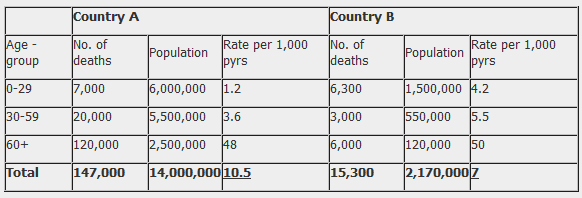
Standardisation Health Knowledge
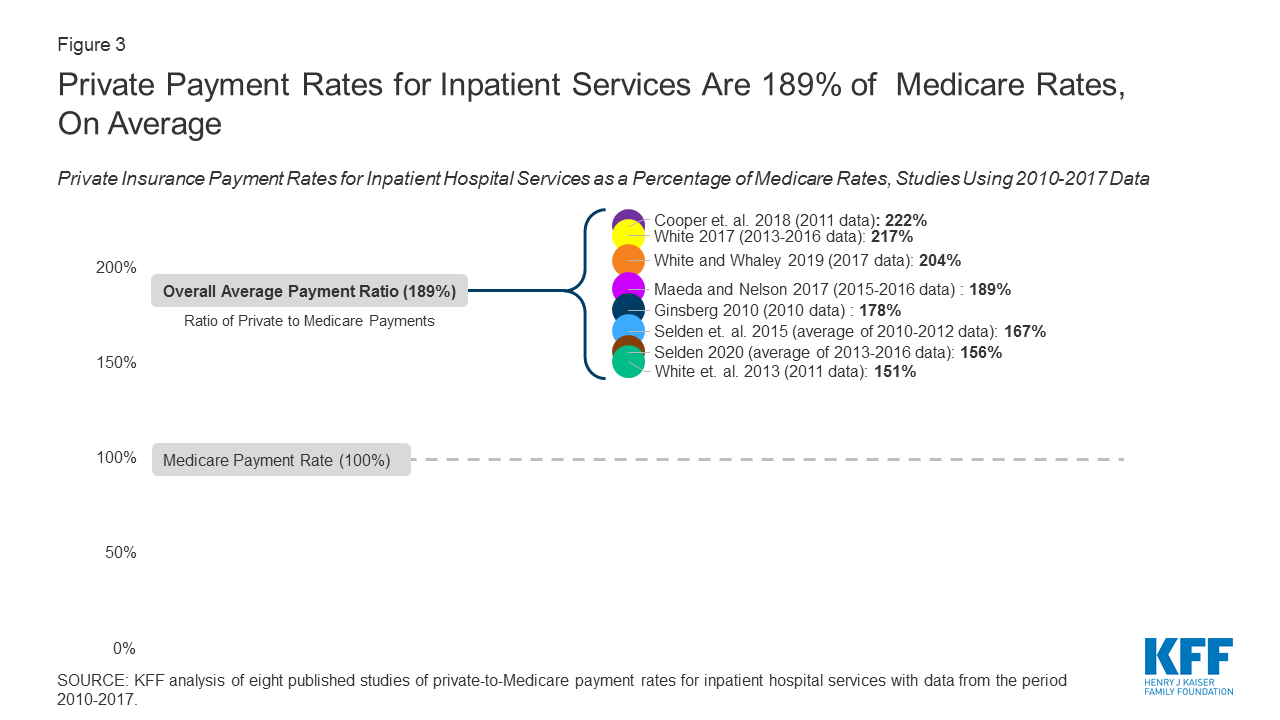
How Much More Than Medicare Do Private Insurers Pay A Review Of The Literature Kff

Numerators Denominators And Populations At Risk Health Knowledge
Numerators Denominators And Populations At Risk Health Knowledge